Lens :
A lens is a portion of a transparent medium bounded by two co-axial spherical refracting surfaces or one spherical and the other plane surface.
Types Of Lenses :
Lenses are divided into two main classes i.e.,
(i) Convex lenses
(ii) Concave lenses
Convex lenses : Convex lenses are thick at the middle and thin at the edges. These lenses make the rays passing through them convergent and are also known as converging lenses.
Concave lenses : Concave lenses are thin at the middle and thick at the edges. These lenses make the rays passing through them divergent and are also known as diverging lenses.

Important Terms Used In Lenses :
1. Centre Of Curvature : The centre of the sphere of which the spherical surface forms a part is called the centre of curvature of that spherical surface.
2. Radius Of Curvature : The radius of the sphere of which the surface forms a part is called the radius of curvature of that spherical surface.

3. Principal axis : The straight line joining the two centres of curvature of a lens is called the principal axis.
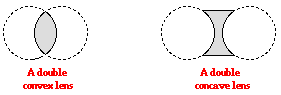

In fig. The line joining C1 and C2, the centre of curvature of two spherical surfaces respectively, is the prinicipal axis.
4. Optical centre : Optical centre of a lens is a point on the principal axis, inside or outside the lens, such that any ray passing through it suffers no deviation. It is represented by O in above fig..
5. Principal focus : A point on the principal axis, where, a number of rays coming parallel to the principal axis after suffering refraction converge to or appear to diverge from is called Principal focus of the lens. It is denoted by F.

6. Focal Length : The distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of lens is called focal length. It is denoted by f. In above fig., the distance CF is the focal length, where O is the optical centre.
The focal length of convex lens is taken as positive whereas the focal length of a concave lens is taken as negative.
7. Aperture : The diameter of the circular boundary of a lens is called the aperture of the lens.
8. Image : If a number of rays starting from a point after suffering refraction through a lens, converge to or appear to diverge from a second point, then this second point is called the image of the first point.
The image formed is real if the rays actually meet at the second point whereas, the image formed is virtual if the rays appear to diverge from the second point.
Courtesy: cnx.org
optics4kids
knowledgebin.org
R.A.Banwat
xamidea
A lens is a portion of a transparent medium bounded by two co-axial spherical refracting surfaces or one spherical and the other plane surface.
Types Of Lenses :
Lenses are divided into two main classes i.e.,
(i) Convex lenses
(ii) Concave lenses
Convex lenses : Convex lenses are thick at the middle and thin at the edges. These lenses make the rays passing through them convergent and are also known as converging lenses.
Concave lenses : Concave lenses are thin at the middle and thick at the edges. These lenses make the rays passing through them divergent and are also known as diverging lenses.

Important Terms Used In Lenses :
1. Centre Of Curvature : The centre of the sphere of which the spherical surface forms a part is called the centre of curvature of that spherical surface.
2. Radius Of Curvature : The radius of the sphere of which the surface forms a part is called the radius of curvature of that spherical surface.

3. Principal axis : The straight line joining the two centres of curvature of a lens is called the principal axis.
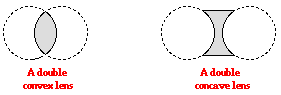

In fig. The line joining C1 and C2, the centre of curvature of two spherical surfaces respectively, is the prinicipal axis.
4. Optical centre : Optical centre of a lens is a point on the principal axis, inside or outside the lens, such that any ray passing through it suffers no deviation. It is represented by O in above fig..
5. Principal focus : A point on the principal axis, where, a number of rays coming parallel to the principal axis after suffering refraction converge to or appear to diverge from is called Principal focus of the lens. It is denoted by F.

6. Focal Length : The distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of lens is called focal length. It is denoted by f. In above fig., the distance CF is the focal length, where O is the optical centre.
The focal length of convex lens is taken as positive whereas the focal length of a concave lens is taken as negative.
7. Aperture : The diameter of the circular boundary of a lens is called the aperture of the lens.
8. Image : If a number of rays starting from a point after suffering refraction through a lens, converge to or appear to diverge from a second point, then this second point is called the image of the first point.
The image formed is real if the rays actually meet at the second point whereas, the image formed is virtual if the rays appear to diverge from the second point.
Courtesy: cnx.org
optics4kids
knowledgebin.org
R.A.Banwat
xamidea
that is the number one time I came to this blog and i discovered a few applicable stuff proper right here. essentially I keen to realize new parameters of writing every-time and someday it turn out to be actually very tough to find such type of platform.
ReplyDeleteic! belin แว่น