Image Formation in Concave Mirror :
Let us discuss the various positions and sizes of images formed by a concave mirror i.e., when objetct is moved from infinity to the pole of concave mirror.
Properties of images :
a) Real image : Image which can be obtained by actual meeting of reflected rays
b) Virtual image: Image resulting from the ( back intersection) of diverging reflected rays.
c) Erect: When the image is straight
d) Inverted : Image upside down
e) Magnified : Larger than object
f) Diminished : Smaller than object
a) Real image : Image which can be obtained by actual meeting of reflected rays
b) Virtual image: Image resulting from the ( back intersection) of diverging reflected rays.
c) Erect: When the image is straight
d) Inverted : Image upside down
e) Magnified : Larger than object
f) Diminished : Smaller than object
(i) When object is at infinity i.e., at infinite distance from the pole of the concave mirror. or when u =  .
.
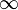 .
.
Image formed will be real and point in size as shown in fig (a).
Case (a): Object placed at infinity

Nature of image: Real, inverted, diminished, at the focus
Case (b): Object placed beyond C, center of curvature i.e., (u>2F)
Nature of image: Real, inverted, diminished image, beyond F and C
Case (c): Object placed at center of curvature
Nature of image: Real, inverted, same size as of object, at centre of curvature
Case (d ): Object placed between Centre of curvature and focus
Nature of image: Real, inverted, same size as of object, at centre of curvature
Case (d ): Object placed between Centre of curvature and focus
Nature of image: Real, inverted, magnified, beyond centre of curvature
Case (e): Object placed at Focus
Nature of image: Real, inverted, highly magnified, at infinity.
Case (e): Object placed at Focus
Nature of image: Real, inverted, highly magnified, at infinity.
Case (f): Object placed between pole and focus
Nature of Image: This is the only case in which we get virtual and erect image. Image is magnified and behind the mirror.
Image Formation in Convex Mirror :
In case of convex mirror for all positions of object ; virtual, erect and diminished image will be formed between pole of the lens and principal focus of the mirror on the other side of the mirror.
(i) When object is at infinity :
In fig (a) below, A virtual point image will be formed at the principal focus of the mirror on the other side of the mirror.
(ii) When Object is placed at 2F :
A virtual, erect and diminished image is formed between P and F on the other side of the mirror in fig.(b)below:
Points to remember:
A plane mirror and a convex mirror always form virtual image whatever be the position of the object.
Courtesy:eonlinetutors
ekshiksha
learnerator.com
meritnation.com
Thanks you cleared up my doubts.....
ReplyDeletehttp://diocesedeilheus.com/optical-center-meilleur-magasin-pour-le-shopping-
ReplyDeleteoptique/